Introduction
Service Binding manages the data plane for applications and backing services. Service Binding Controller reads data made available by the control plane of backing services and projects the data to applications according to the rules provided via ServiceBinding resource.
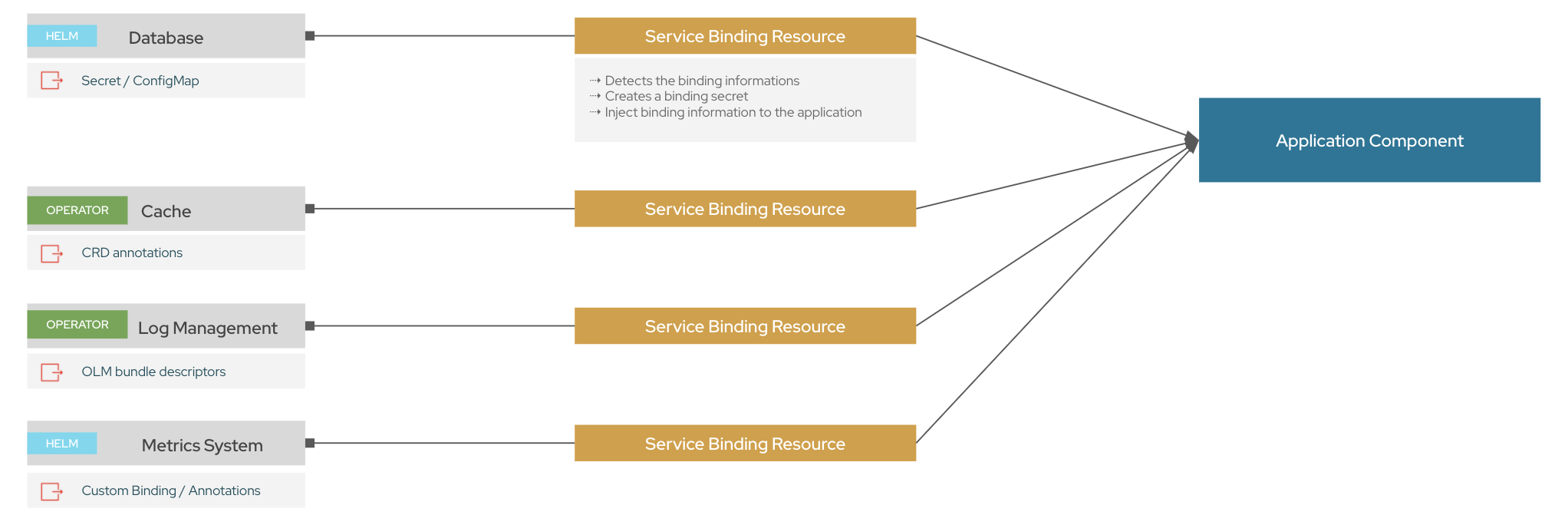
Why Service Bindings?
Today in Kubernetes, the exposure of secrets for connecting applications to external services such as REST APIs, databases, event buses, and many more is manual and bespoke. Each service provider suggests a different way to access their secrets, and each application developer consumes those secrets in a custom way to their applications. While there is a good deal of value to this flexibility level, large development teams lose overall velocity dealing with each unique solution.
Service Binding:
-
Enables developers to connect their application to backing services with a consistent and predictable experience
-
Removes error-prone manual configuration of binding information
-
Provides service operators a low-touch administrative experience to provision and manage access to services
-
Enriches development lifecycle with a consistent and declarative service binding method that eliminates environments discrepancies
Features
Application Projection
-
Projection of binding data as file, with a volume mount
-
Projection of binding data as environment variables
Extracting Binding data from Services
-
Extract binding data based on annotations present in CRDs/CRs/resources
-
Extract binding data based on annotations present in OLM descriptors
Service Binding Options
-
Cross-namespace binding
-
Binding to a specific container of an application
-
Custom path projection
-
Secret substitution and mappings with Go Template
-
Auto-detection of bindings in the absence of binding decorators
-
Binding of PodSpec or non-PodSpec workloads
-
Custom binding variables composed from one or more backing services
Referenced Specification
Service Binding Operator supports the Service Binding Specification for Kubernetes.